PT TESTINDO
JL. Radin Inten II no. 61 B Duren Sawit, Jakarta 13440
Mobile / WHATSAPP: 0813 9929 1909
PIN BB: 580EC93D
Phone. 021-29563045
Fax. 021-29563052
Email: sales@testindo.com
Website: www.testindo.com
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
|
|
||||||||
| Factors Influencing Test Methods | |||||||||
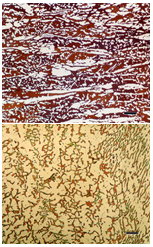
 Some weldline cracks, such as this one shown above, may be detected by both eddy current and ultrasonic equipment. Some weldline cracks, such as this one shown above, may be detected by both eddy current and ultrasonic equipment. |
 Factors
that influence system selection include the capabilities and
limitations of each technology, as well as the diameter, wall thickness,
tube condition, and throughput speed of the product under test. Where
the test is applied in the manufacturing cycle also influences the
choice of method and apparatus. This can range from tests limited to the
heat affected zone on the weld mill with perhaps an in-line anneal, to
full body inspection of cut lengths after drawing and annealing or other
heat treating. Each test method has inherent capabilities and
limitations that are different. Factors
that influence system selection include the capabilities and
limitations of each technology, as well as the diameter, wall thickness,
tube condition, and throughput speed of the product under test. Where
the test is applied in the manufacturing cycle also influences the
choice of method and apparatus. This can range from tests limited to the
heat affected zone on the weld mill with perhaps an in-line anneal, to
full body inspection of cut lengths after drawing and annealing or other
heat treating. Each test method has inherent capabilities and
limitations that are different. |
||||||||
 |
Common Defects Detected | ||||||||
| Generally, for tube
applications that require high throughput speeds, eddy current is the
preferred method to detect small, short, incomplete welds,and some
subsurface cracks in carbon steel or non ferrous tube. For full body
tests, including the detection of long, continuous defects such as
incomplete seam welds in tube, and inclusions, voids or cavities,
ultrasonic test systems are recommended. Flux leakage systems are
available to accurately detect longitudinal and transverse surface
defects on the OD and ID of heavy-wall magnetic tubing. |
|||||||||
| The picture above shows a short pinhole flaw that was detected by eddy current, but was difficult to detect using ultrasonic tests. | |||||||||
 |
Weld Types | ||||||||
| The process of ERW and
Induction welding is preferred for most carbon and alloy steel. Defects
that may arise include all of those previously mentioned. TIG welding is
a slow process usually used for stainless steel or titanium. Incomplete
ID weld defects are a common concern in this process. Laser welding is a
much faster process used for stainless steel, titanium, duplex and
nickel alloys. Typical defects include very short pinholes, and long
continuous ID defects such as incomplete or miss-match welds. |
|||||||||
| This picture above shows a cross section of a tube wall with a long, continuous poor ID weld that was detected by ultrasonic methods, but not by eddy current. | |||||||||
| DOWNLOAD PDF | |||||||||

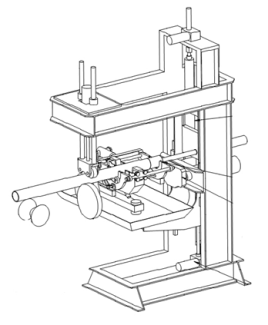 The Echomac® UT End Tester consists of two
The Echomac® UT End Tester consists of two MAC’s highly trained and knowledgeable engineers, field staff, and
representatives provide superior NDT equipment, services, and training
worldwide.
MAC’s highly trained and knowledgeable engineers, field staff, and
representatives provide superior NDT equipment, services, and training
worldwide.
 Download PDF
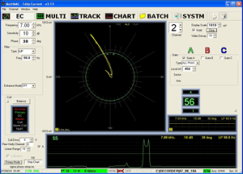
Download PDF| · 2507 Duplex Stainless Steel Tube
· 80 FT Cut Lengths · 3/4″ OD with .083″ Wall Thickness · Detects Sigma Phase as Small as 2.6% of Tube Wall Cross Section · 2 Channel MultiMac® Eddy Current Tester- Offline · 2 Varimac® Comparator Coils |

 The test consists of a 2 channel MultiMac®
coil eddy current tester. 1 channel is used for the detection of
typical defects, while the other channel is used for finding sigma
phase; a condition caused from improper or extensive heat treatment.The second channel on the MultiMac is an absolute tester using two Varimac® coils. One coil is balanced on air and used to calibrate the equipment with a reference standard.
The test consists of a 2 channel MultiMac®
coil eddy current tester. 1 channel is used for the detection of
typical defects, while the other channel is used for finding sigma
phase; a condition caused from improper or extensive heat treatment.The second channel on the MultiMac is an absolute tester using two Varimac® coils. One coil is balanced on air and used to calibrate the equipment with a reference standard.